Eta-squared
Because of the relationship between ANOVA and multiple regression, we can use the correlation coefficient as a measure of effect size in ANOVA. The value of the correlation coefficient is given by Multiple R in the Regression data analysis tool. E.g., for Example 1 of ANOVA using Regression, r = .285 (see Figure 2 of ANOVA using Regression), which indicates a medium effect.
A more commonly used measure of effect size is the coefficient of determination R2 which in the context of ANOVA is called eta squared, labeled η2. Thus
For the above example, η2 = .0812, which means that 8.12% of the variance is explained by the model.
Note too that since for one factor ANOVA
it follows that
Thus
![]()
η2 = .01 is considered a small effect and η2 = .06 and .14 are considered medium and large effects respectively.
Omega-squared
Unfortunately, eta squared is a biased estimate of the population’s coefficient of determination. A less biased estimate, called omega squared, is a better measure of effect size. Omega squared is given by the following formulas:
The first version uses the terminology of regression analysis, while the second uses the terminology of ANOVA. Since the numerator can be expressed as
we have the following alternative form:
For one-factor ANOVA in Example 3 of Basic Concepts for ANOVA, ω2 = 0.14 (as can be seen in Figure 1 of Confidence Interval for ANOVA).
In general, ω2 is a more accurate measure of the effect than η2. Once again, ω2 = .01 is considered a small effect and ω2 = .06 and .14 are considered medium and large effects respectively.
Partial eta-squared and partial omega-squared
Another commonly used measure of effect size is partial eta-squared, which is defined as:
Clearly, for one factor ANOVA, eta-squared and partial eta-squared have the same value.
Similarly there is a partial omega-squared version of ω2, which is defined as
But since the denominator can be expressed as
![]()
once again, for a one factor ANOVA, partial omega-squared is equal to omega-squared.
Cohen’s f
Another measure of effect size is Cohen’s f effect size that can be calculated by
Note that
In Effect Size for ANOVA, we described a version of Cohen’s f effect size by
These two versions are almost equal. In fact
Note too that if f is known, then eta-square can be expressed as
η2 = f2/(f2+1)
Effect size for post-hoc tests
Effect sizes for the omnibus ANOVA results, however, are not really that interesting. More useful are effect sizes for the follow-up tests. As explained in Linear Regression for Comparing Means, a useful measure of effect size here is
![]()
Examples Workbook
Click here to download the Excel workbook with the examples described on this webpage.
References
Lakens, D. (2015) Why you should omega-squared instead of eta-squared. The 20% Statistician
http://daniellakens.blogspot.com/2015/06/why-you-should-use-omega-squared.html
Carroll, R. M., Nordholm, L. A. (1975). Sampling characteristics of Kelley’s ε and Hays’ ω. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 35(3), 541–554.
Available through Sage Journals
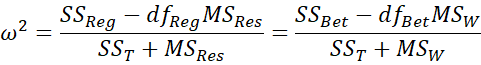
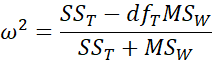
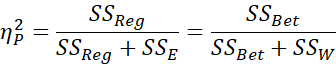
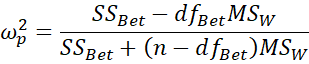
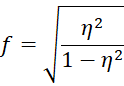
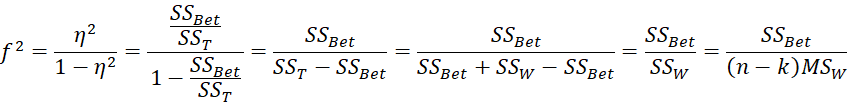
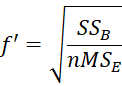
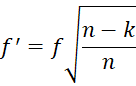
Hello Mr. Professor. I need your help on how to calculate the effect size and standard error from the Anova table. I do not know the statistical terms very well. could you please give me an example with the following data. thanks a lot in advance.
total N(size):131
Df:24
whitin group: 1115,42
between-group: 2371,823
total:3487,242
F:1,336
p: ,162
thank you.
I suggest that you look at the following webpage:
https://real-statistics.com/one-way-analysis-of-variance-anova/effect-size-anova/
There is a link towards the bottom of the webpage that shows how to calculate the effect size for the example shown on that webpage.
Charles